Bypassing Dependency Errors with Dummy Packages
Fixing Missing or Renamed Dependencies When Installing .deb Packages on Kali Linux
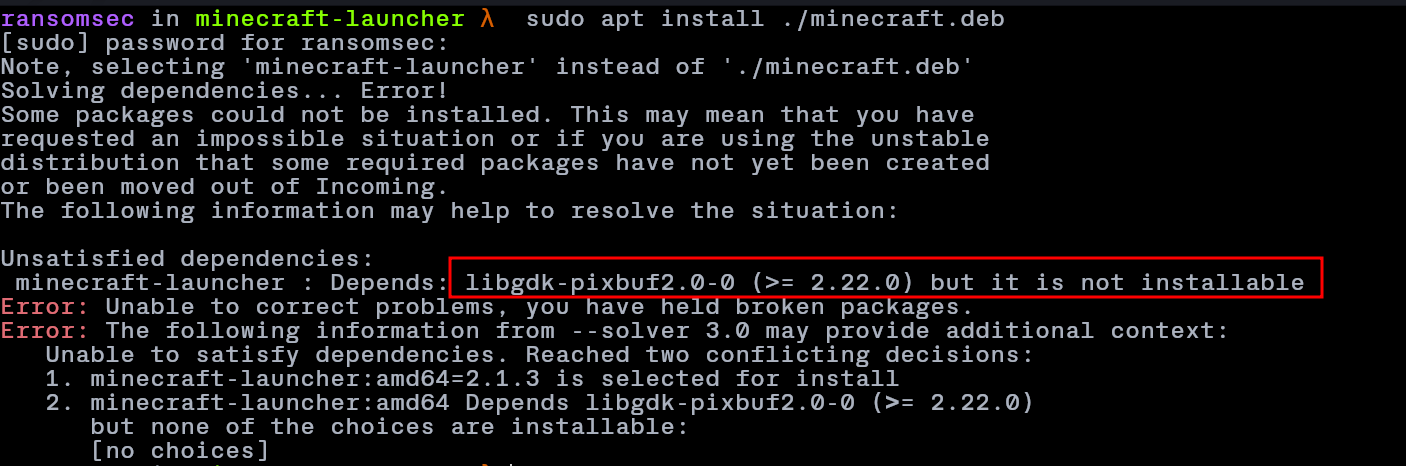
While installing minecraft .deb packages on Kali Linux (or other Debian-based distros), i encounter this dependency errors like:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Unsatisfied dependencies:
minecraft-launcher : Depends: libgdk-pixbuf2.0-0 (>= 2.22.0) but it is not installable
Error: Unable to correct problems, you have held broken packages.
Error: The following information from --solver 3.0 may provide additional context:
Unable to satisfy dependencies. Reached two conflicting decisions:
1. minecraft-launcher:amd64=2.1.3 is selected for install
2. minecraft-launcher:amd64 Depends libgdk-pixbuf2.0-0 (>= 2.22.0)
but none of the choices are installable:
[no choices]
This usually happens because:
- The
.debwas built for an older Debian-based distro version. - Some library package names have changed or been replaced in newer Kali/Debian releases.
- System actually has the library, but under a different package name. For example installer needs the version
libgdk-pixbuf2.0-0but your system havelibgdk-pixbuf-2.0-0
Why Does This Happen?
Package maintainers sometimes rename libraries as they evolve. For example:
- The package
libgdk-pixbuf2.0-0might have been renamed tolibgdk-pixbuf-2.0-0in newer distros. - The
.debfile (minecraft) still demands the old package name, soaptrefuses to install.
But the package is already installed in my machine with different name:

Sometimes apt install ./package.deb Fails, But dpkg -i ./package.deb Works
aptperforms strict dependency checks and will refuse to install the package if dependencies can’t be met.dpkgjust installs the package without resolving dependencies, so it succeeds but leaves broken dependencies.- You can then run
sudo apt --fix-broken installto fix what’s missing — but if the exact package name doesn’t exist, this often fails or removes the package.
The Clean Workaround: Using a Dummy Package with equivs
You can create a dummy package to fake the missing dependency, telling apt it’s installed — while your system already has the real functionality under a differently named package.
Step-by-step:
- Install
equivs:
1
sudo apt install equivs
- Create a working directory and control file:
1
2
mkdir ~/dummy-pkg && cd ~/dummpy-pkg
equivs-control missing-lib-name
- Edit
missing-lib-namewith your favorite editor (e.g.vim), replacing the contect with:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
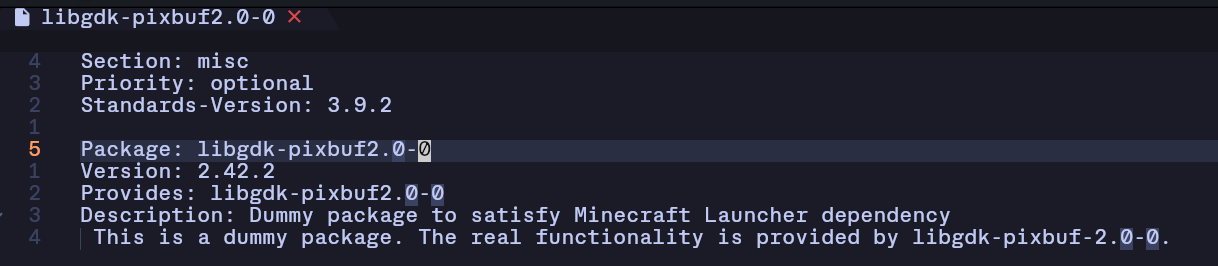
Section: misc
Priority: optional
Standards-Version: 3.9.2
Package: missing-lib-name
Version: 1.0 // insert the version No. that is missing
Provides: missing-lib-name
Description: Dummy package to satisfy missing dependency
This is a dummy package. The actual functionality is provided by a different package.
- Build and install the dummy package:
1
2
equivs-build missing-lib-name
sudo apt install ./missing-lib-name_1.0_all.deb
Why this works: A simple Analogy
Imagine Minecraft is a guest who insists they won’t come to the party unless “DJ Mike” is there. But you already have “DJ Michael” playing — they’re the same person, just a different name.
So you throw a cardboard cutout labeled “DJ Mike” in the corner.
Now Minecraft walks in and says: “Oh cool, DJ Mike’s here. Let’s party.”
Wrapping Up
This tricks lets you bypass pacakge naming mismatches and get legacy or third-party .deb files working on Debian based linux distros.
NOTE: Only use dummpy package when you are confident the real func exists on your system under another package.